Automatic mixing
Dissonance suppression during harmonic mixing
A journey through the DJ world
by Stefan Hamburger
July 2017
Seminar Topics in Computer Music
Prof. Paolo Bientinesi, RWTH Aachen
What is automatic mixing?
Generating a continuous stream of music with smooth transitions
Track A → Track B
DJs in a club
History of DJing
Francis Grasso: beatmatching

Technics SL-1200 (1971)
History of DJing

1986: Harmonic Keys magazine (Stuart Soroka)

History of DJing
Camelot Sound (Mark Davis)
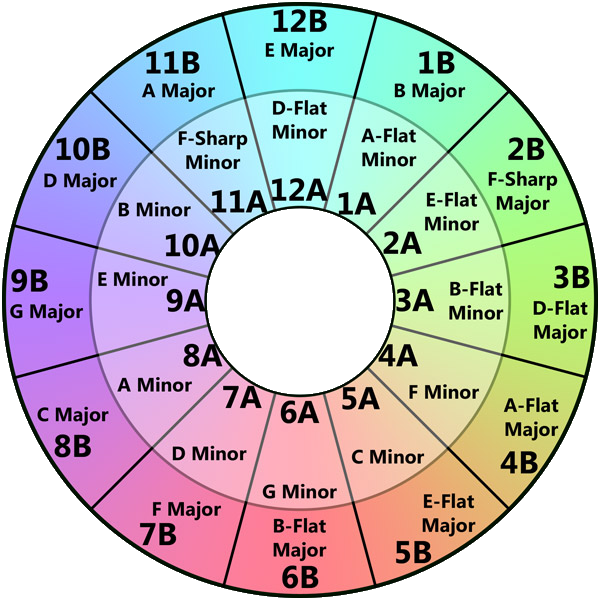
EasyMix wheel
History of DJing
- 1999: first DJ software
- 2006: harmonic mixing software
Mixxx software
What is harmony?
Universal to all humans,
but varies based on personal experience
Music theory
| Consonant intervals: octave, perfect fifth, major third |
Dissonant intervals: semitone, tritone |
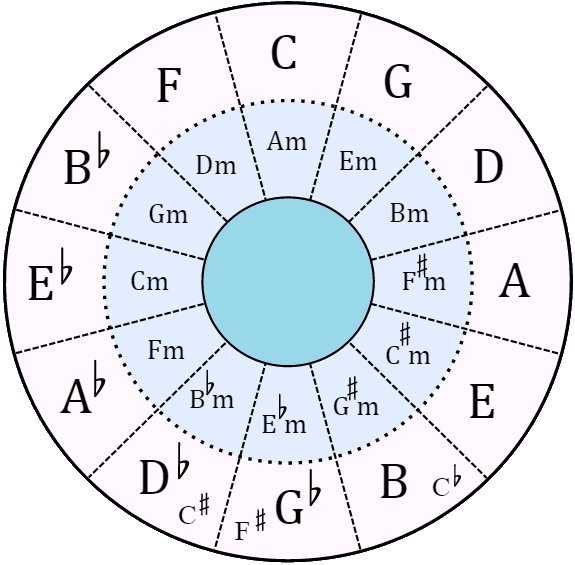
Circle of Fifths (Quintenzirkel)
Psychoacoustics
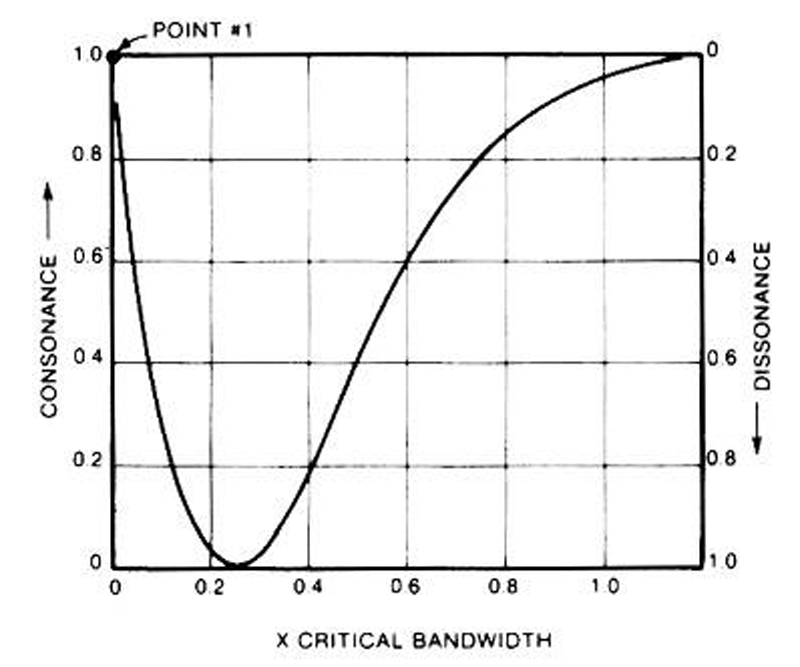
Roughness
Critical bandwidth
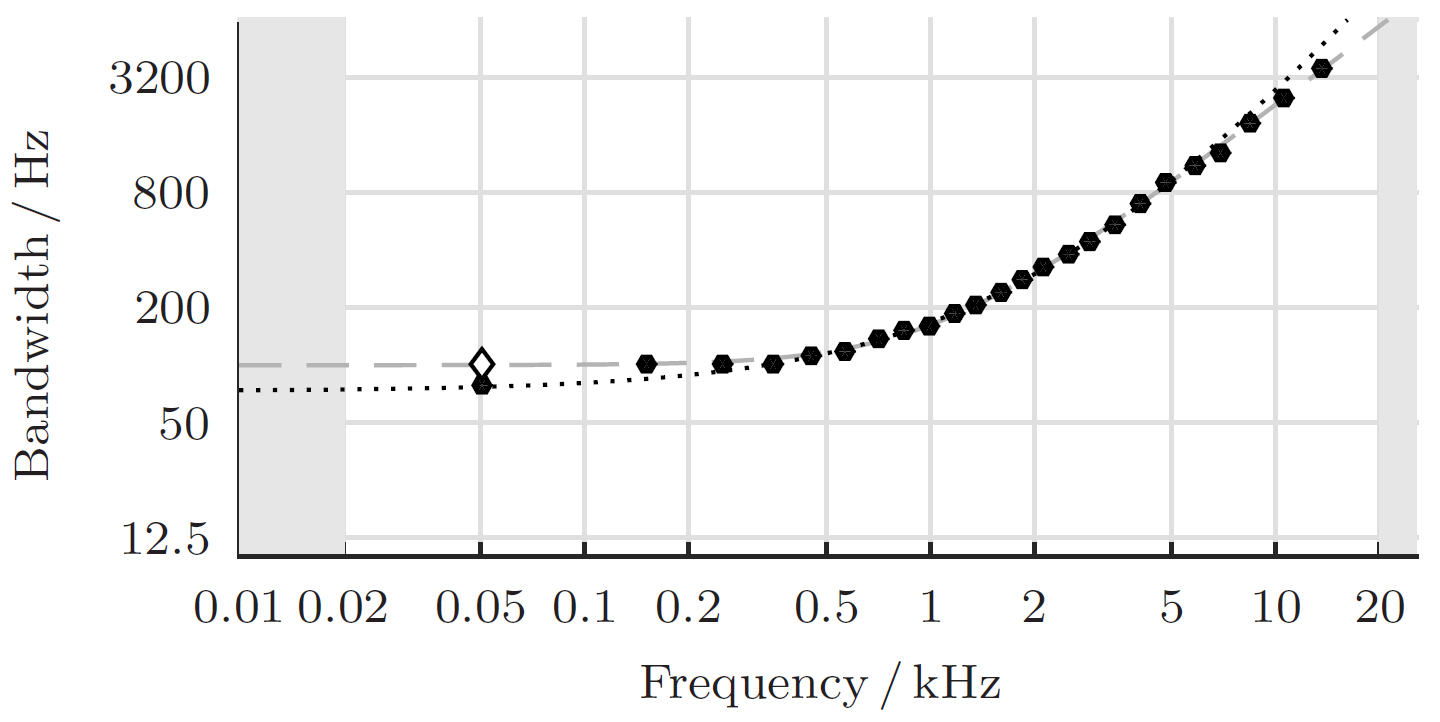
$$CBW(f) = 25 + 75 \cdot (1 + 1.4 \cdot (\frac{f}{1000})^2)^{0.69}$$
Zwicker (1961), Zwicker and Terhardt (1980)
Roughness
Given: $$f_1, f_2$$
$$\color{lime}{y} = \frac{\left|f_2 - f_1\right|}{CBW(\frac{f_1 + f_2}{2})}$$
$$Roughness(f_1, f_2) = max(\underbrace{(e^1 \cdot \frac{\color{lime}{y}}{0.25} \cdot e^{-\frac{\color{lime}{y}}{0.25}})^2}_{\color{gray}{= 16 y^2 \cdot e^{2-8y}}}, 0) \in [0, 1]$$
Harmonic series
(Naturtonreihe)
Fundamental frequency $$f$$
$$f, 2f, 3f, 4f, 5f, \ldots$$
Octave equivalence
$$\ldots \overset{\wedge}{=} A_4 \overset{\wedge}{=} A_5 \overset{\wedge}{=} A_6 \overset{\wedge}{=} \ldots$$
$$\ldots \overset{\wedge}{=} 440 Hz \overset{\wedge}{=} 880 Hz \overset{\wedge}{=} 1760 Hz \overset{\wedge}{=} \ldots$$
Tones and semitones
$$f + 2f + 3f + 4f + 5f + \ldots$$
$$f + \ldots + 1.25f + \ldots + 1.5f + \ldots + 1.75f + \ldots + 2f$$
12 semitones: A, A#, B, C, C#, D, D#, E, F, F#, G, G#
Tuning
Equal temperament (12-TET)
$$f_i = 440\ Hz \cdot 2^{\frac{i}{12}}, i \in \mathbb{Z}$$
| Tone | $$A_4$$ | $${A\sharp}_4$$ | $$B_4$$ | $$C_4$$ | $${C\sharp}_4$$ | $$D_4$$ | $${D\sharp}_4$$ | $$E_4$$ | $$F_4$$ | $${F\sharp}_4$$ | $$G_4$$ | $${G\sharp}_4$$ | $$A_5$$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hertz | 440 = 440 |
466.16 | 493.88 | 523.25 | 554.37 ≈ 550 |
587.33 | 622.25 | 659.26 ≈ 660 |
698.46 | 739.99 | 783.99 | 830.61 | 880 = 880 |
Roughness
Given two complex tones
$$\color{orange}{T_1 = \{(a_1, f_1), (a_2, f_2), (a_3, f_3), \dots \}},$$
$$\color{lime}{T_2 = \{(a_4, f_4), (a_5, f_5), (a_6, f_6), \dots \}}$$
$$Roughness(T_1, T_2) = \frac{\sum\limits_{\color{orange}{(a_i, f_i) \in T_1}} \sum\limits_{\color{lime}{(a_j, f_j) \in T_2}} \color{orange}{a_i} \cdot \color{lime}{a_j} \cdot Roughness(\color{orange}{f_i}, \color{lime}{f_j})}{\sum\limits_{\color{orange}{(a_i, f_i) \in T_1}} \sum\limits_{\color{lime}{(a_j, f_j) \in T_2}} \color{orange}{a_i} \cdot \color{lime}{a_j}} \color{gray}{\in [0, 1]}$$
Previous approaches
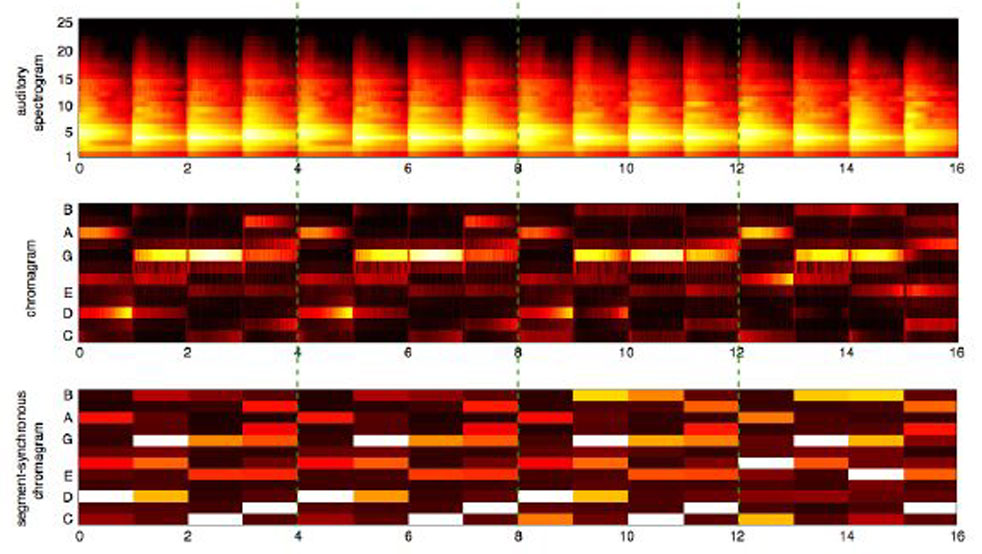
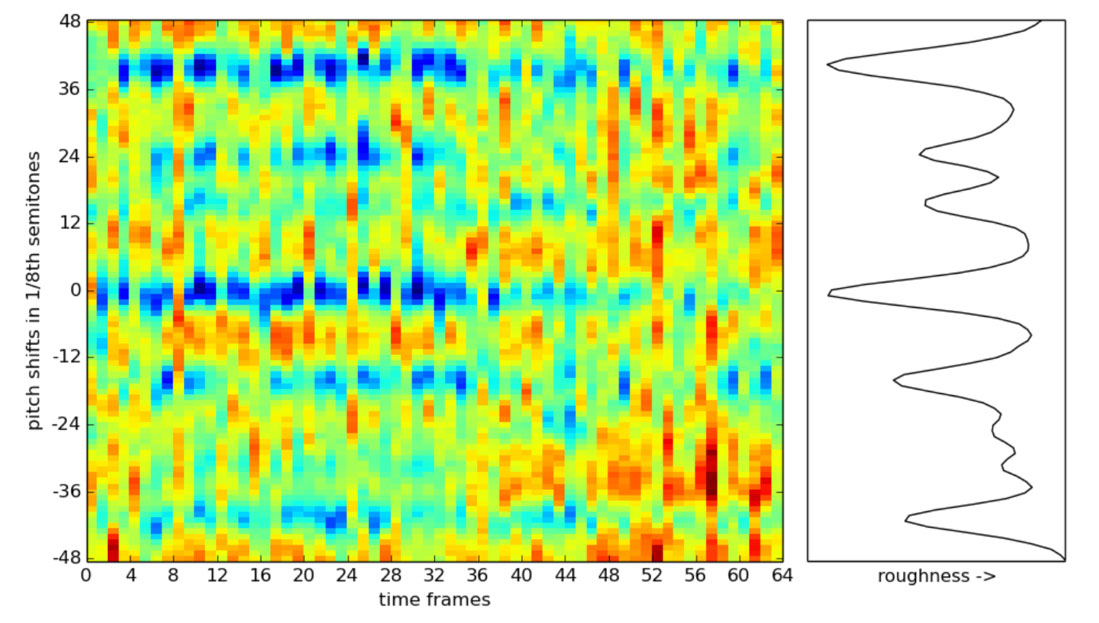
Key estimation

Chroma based
Roughness based
“Techniques for
automatic dissonance suppression
in harmonic mixing”
Master thesis by Vittorio Maffei (2014-2015)
Preprocessing
Tracks converted to mono, 44,100 Hz
Tempo changed to 120 bpm
8 second samples = 16 beats
Short time Fourier transform (STFT)
Blackman window
4096 window size, 256 hop size
4096 bins, 5000 Hz max frequency
→ 20 strongest partials extracted
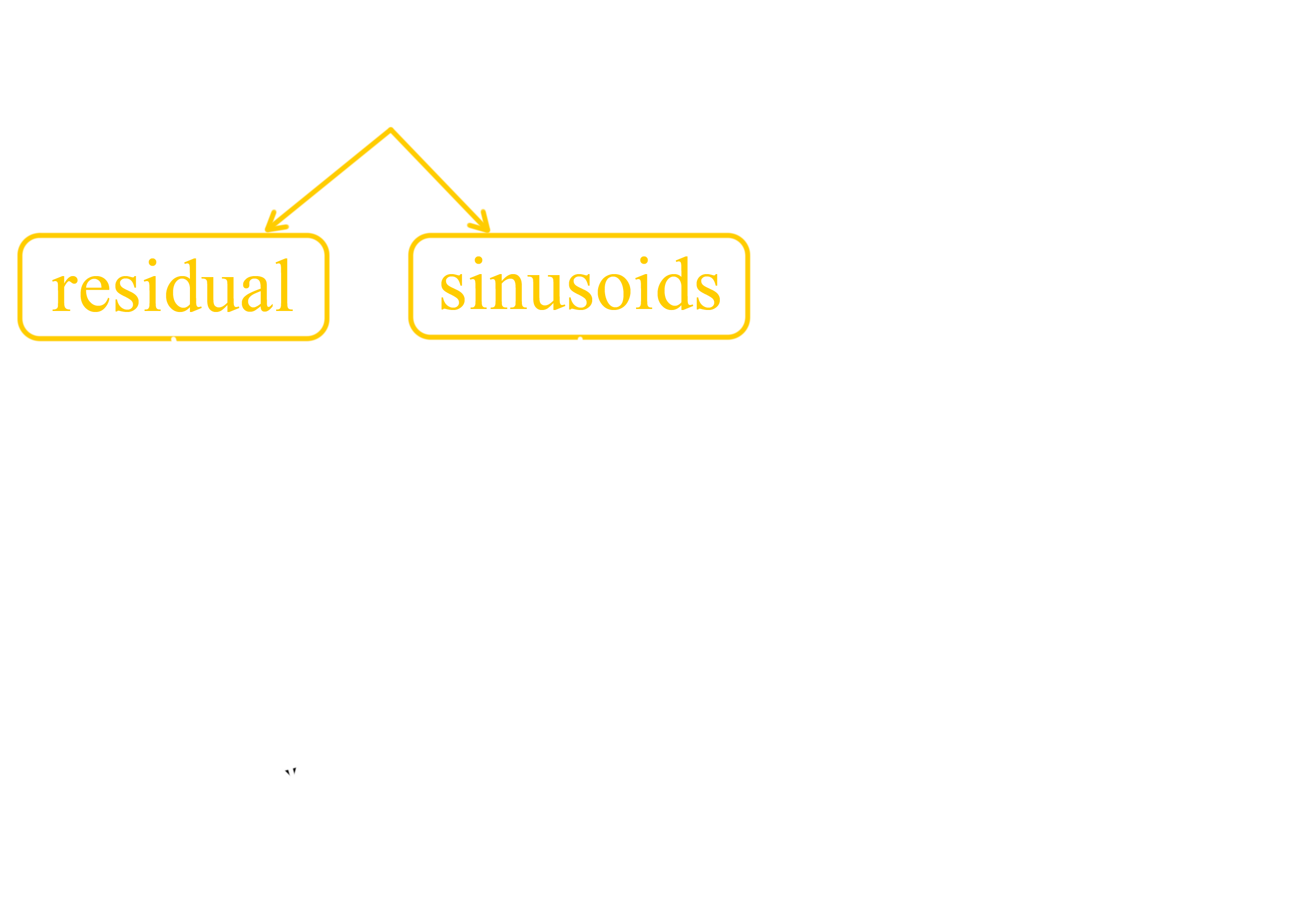
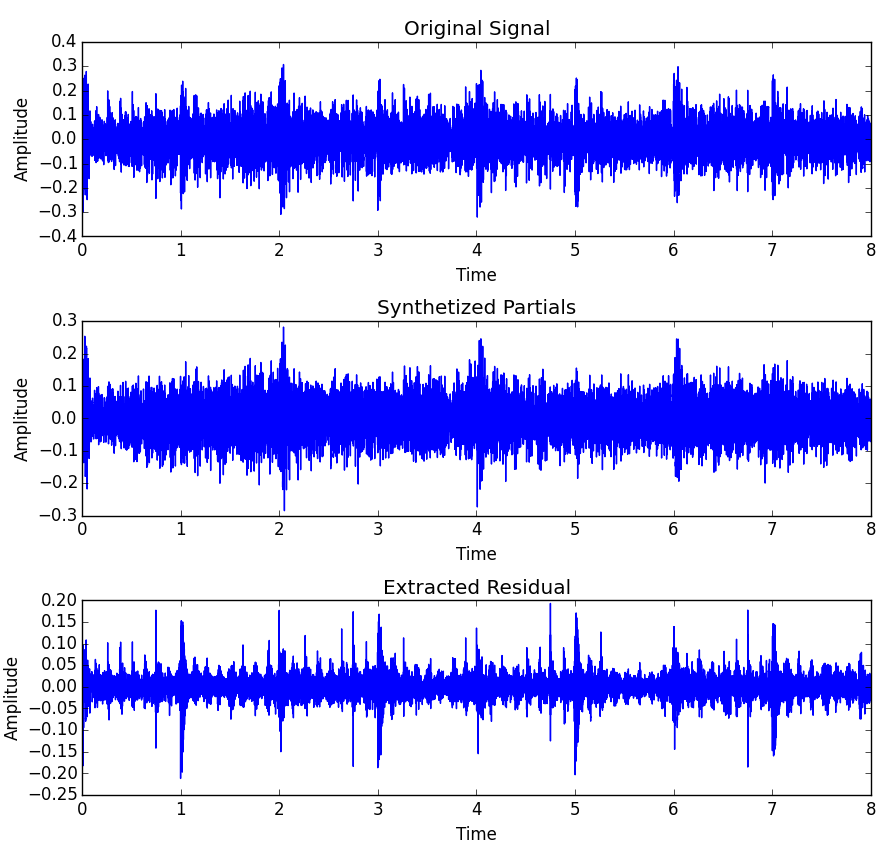
Residual extraction
Split signal into sinusoids and residuals
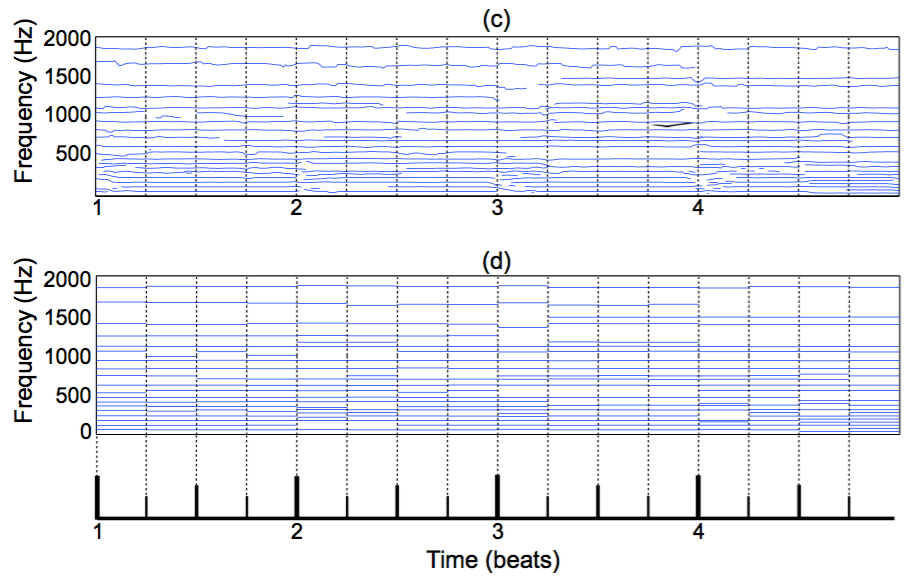
Temporal averaging
Averaged to 16th notes
1379 windows → 64 windows
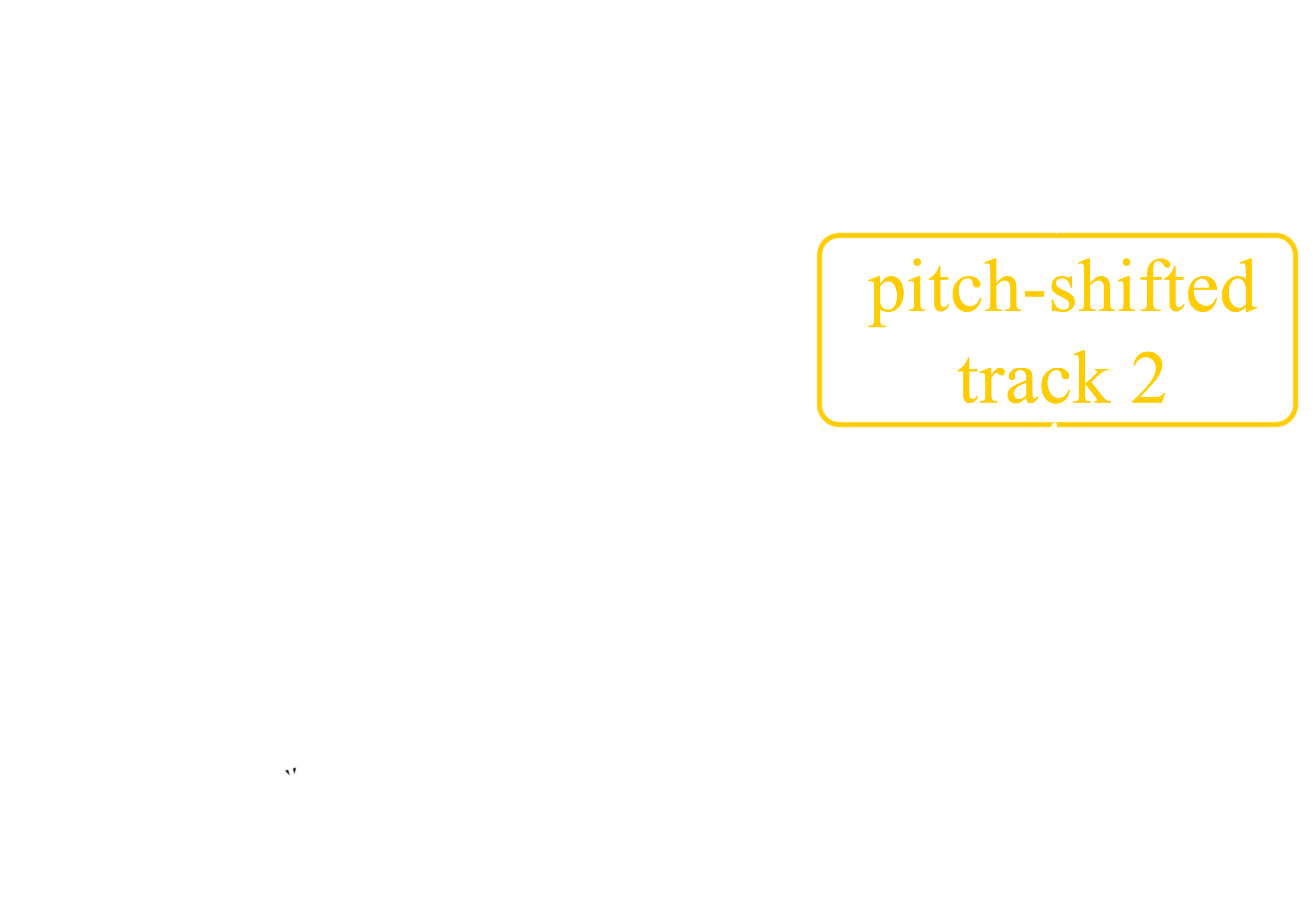
Optimal pitch-shift

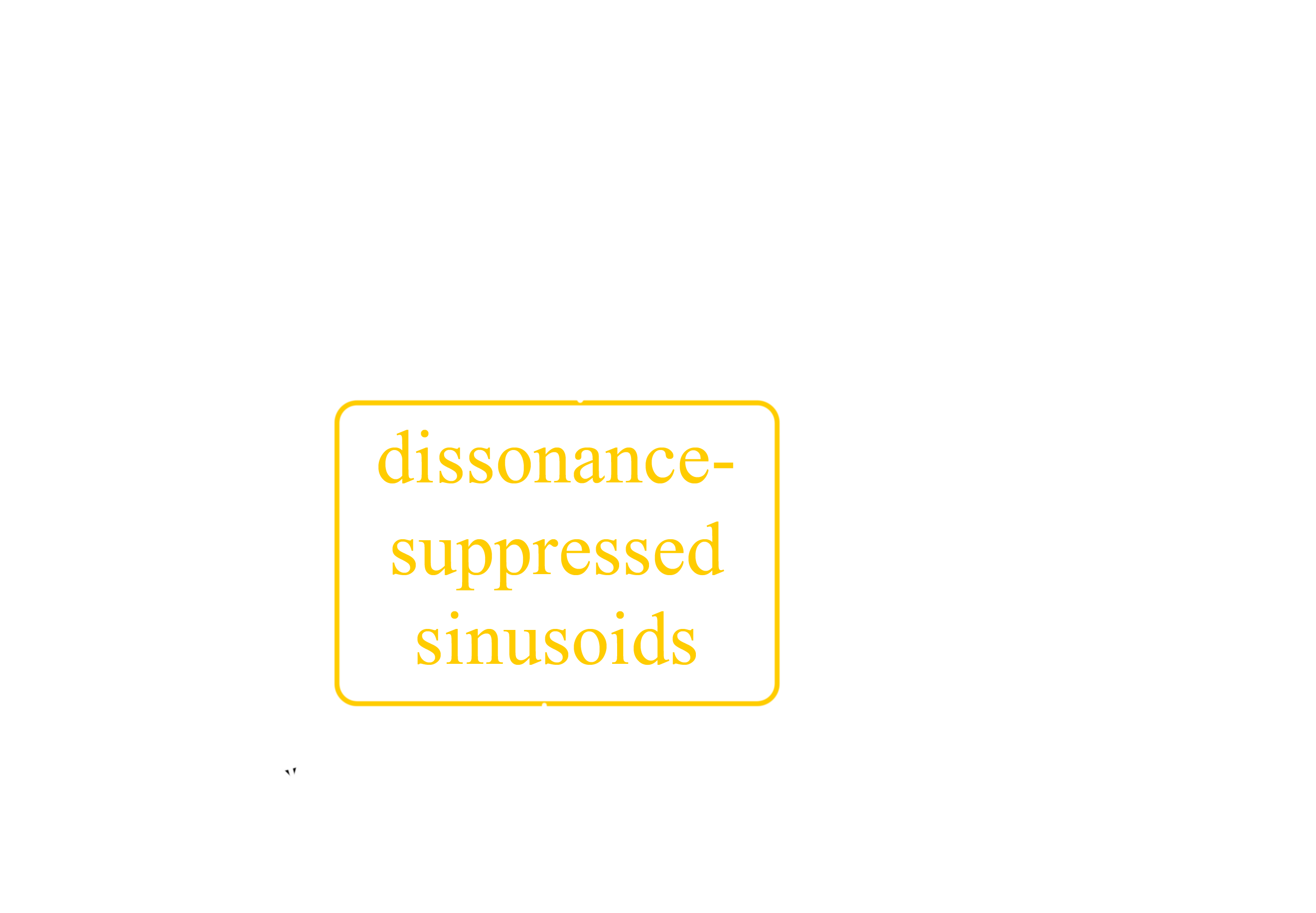
Dissonance suppression
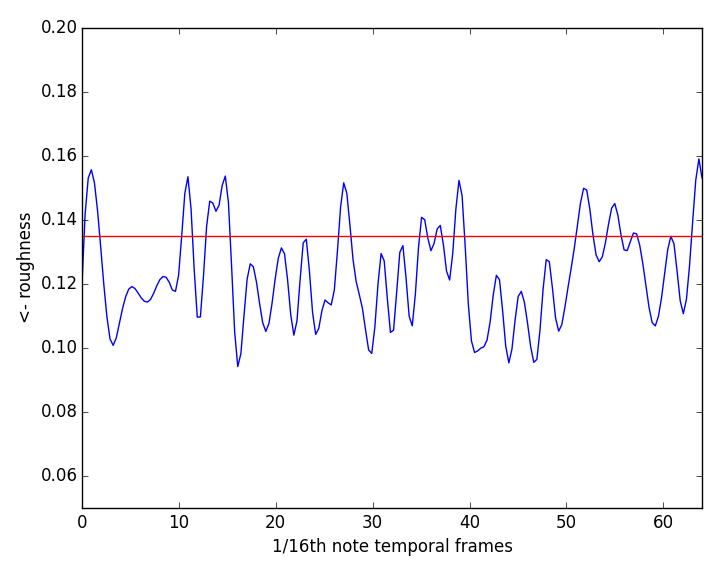
Partials suppression

Results
- Improvements to disharmonic mixes
- No changes to already harmonic mixes
Criticism
- Only tested on 8 second fragments
- Only tested by musically trained listeners
- No audio samples provided
- Used existing libraries, did not build a new tool
- Many typos
Future work?
- Machine learning
- Volume/loudness adjustment
Obligatory Sources
- Papers
- Vittorio Maffei: Techniques for automatic dissonance suppression in harmonic mixing. Master thesis at University of Milan, 2015.
- Richard Parncutt: Harmony: A Psychoacoustical Approach. Springer 1989.
- Florian Völk: Updated analytical expressions for critical bandwidth and critical-band rate. DAGA 2015, Nuremberg.
- Dave Cliff: Hang the DJ: Automatic Sequencing and Seamless Mixing of Dance-Music Tracks. HP Laboratories Bristol, 2000.
- Harmonic Keys magazine. 1986-1987.
- Videos
- Howard Goodall: How Music Works. 4-part TV series on Channel 4 (UK), 2006.
- William Cox: Timeseries Data Superpowers: Intuitive Understanding of FIR Filtering and Fourier Transforms. OSCON 2014.
- Meinard Müller, Peter Grosche: Tempo and Beat Tracking. AudioLabs Erlangen, 2016.
- Tony Prince: The History of DJ. Video series by DMC.
- CD Projekt Red: The Witcher 3 : Wild Hunt. Music: General Approach. Wwise Tour 2016, Warsaw.
- PCDJ: various press videos from 2000
- Leonard Bernstein: The Unanswered Question. Lecture series at Harvard, 1973.
- Websites
- Camelot Sound, company website.
- Web Audio API, MDN Web Docs.
- For a complete list of sources, see the slide notes.
Takeaways
- Roughness measure
(¼ of CBW = most dissonant) - Harmonic series
($f, 2f, 3f, \ldots$)
5 minutes of harmonic mixing (demo for Mixed in Key):